सीपीयू सॉकेट: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
! style="text-align:left;| पीजीए 168 | ! style="text-align:left;| पीजीए 168 | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| इंटेल [[80486]]<br />एएमडी 486<br /> | | इंटेल [[80486]]<br />एएमडी 486<br />सिरिक्स 486 | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 1|सॉकेट 1]] | ! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 1|सॉकेट 1]] | ||
| 1989 | | 1989 | ||
| इंटेल [[80486]]<br />एएमडी 486<br />एएमडी 5x86<br /> | | इंटेल [[80486]]<br />एएमडी 486<br />एएमडी 5x86<br />सिरिक्स 486<br />सिरिक्स 5x86 | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 2|सॉकेट 2]] | ! style="text-align:left;| [[Socket 2|सॉकेट 2]] | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| इंटेल [[80486]]<br />इंटेल | | इंटेल [[80486]]<br />इंटेल पेंटियम Overdrive (P24T)<br />इंटेल DX4<br />एएमडी 486<br />एएमडी 5x86<br />सिरिक्स 486<br />सिरिक्स 5x86 | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 3|सॉकेट 3]] | ! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 3|सॉकेट 3]] | ||
| 1991 | | 1991 | ||
| इंटेल [[80486]]<br />इंटेल | | इंटेल [[80486]]<br />इंटेल पेंटियम Overrdrive (P24T)<br />इंटेल DX4<br />एएमडी 486<br />एएमडी 5x86<br />सिरिक्स 486<br />सिरिक्स 5x86<br />IBM Blue Lightning | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 4|सॉकेट 4]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 4|सॉकेट 4]] | ||
| 1993 | | 1993 | ||
| इंटेल [[Intel P5| | | इंटेल [[Intel P5|पेंटियम]] | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 5|सॉकेट 5]] | ! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 5|सॉकेट 5]] | ||
| 1994 | | 1994 | ||
| इंटेल [[Intel P5| | | इंटेल [[Intel P5|पेंटियम]]<br />[[Advanced Micro Devices|एएमडी]] [[AMD K5|K5]]<br />[[Cyrix|सिरिक्स]] [[Cyrix 6x86|6x86]]<br />[[Integrated Device Technology|IDT]] [[WinChip]] C6<br />[[Integrated Device Technology|IDT]] [[WinChip]] 2 | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 7|सॉकेट 7]] | ! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 7|सॉकेट 7]] | ||
| 1994 | | 1994 | ||
| इंटेल [[Intel P5| | | इंटेल [[Intel P5|पेंटियम]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium MMX|पेंटियम MMX]]<br />एएमडी [[AMD K6|K6]] | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 8|सॉकेट 8]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 8|सॉकेट 8]] | ||
| 1995 | | 1995 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium Pro]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium Pro|पेंटियम Pro]] | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Slot 1]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Slot 1]] | ||
| 1997 | | 1997 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium II]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium II|पेंटियम II]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III|पेंटियम III]] | ||
| Desktop | | Desktop | ||
| [[Edge connector|Slot]] | | [[Edge connector|Slot]] | ||
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| 66–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | | 66–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| Celeron (Covington, Mendocino)<br /> | | Celeron (Covington, Mendocino)<br />पेंटियम II (Klamath, Deschutes)<br />पेंटियम III (Katmai)- all versions<br />पेंटियम III (coppermine) | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
! style="text-align:left;| [[Super Socket 7|Super सॉकेट 7]] | ! style="text-align:left;| [[Super Socket 7|Super सॉकेट 7]] | ||
| 1998 | | 1998 | ||
| एएमडी [[AMD K6-2|K6-2]]<br />एएमडी [[AMD K6-III|K6-III]]<br />[[Rise Technology|Rise]] [[mP6]]<br /> | | एएमडी [[AMD K6-2|K6-2]]<br />एएमडी [[AMD K6-III|K6-III]]<br />[[Rise Technology|Rise]] [[mP6]]<br />सिरिक्स [[Cyrix 6x86|MII]] | ||
| | | | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Slot 2]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Slot 2]] | ||
| 1998 | | 1998 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium II Xeon]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III Xeon]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium II Xeon|पेंटियम II Xeon]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III Xeon|पेंटियम III Xeon]] | ||
| Server | | Server | ||
| [[Edge connector|Slot]] | | [[Edge connector|Slot]] | ||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | सॉकेट 615 | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | सॉकेट 615 | ||
| 1999 | | 1999 | ||
| इंटेल [[Mobile Pentium II]]<br />इंटेल [[Mobile Celeron]] | | इंटेल [[Mobile Pentium II|Mobile पेंटियम II]]<br />इंटेल [[Mobile Celeron]] | ||
| Notebook | | Notebook | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 370|सॉकेट 370]] | ! style="text-align:left;"| [[Socket 370|सॉकेट 370]] | ||
| 1999 | | 1999 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium III]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />[[VIA Technologies|VIA]] [[Cyrix III]]<br />[[VIA Technologies|VIA]] [[VIA C3|C3]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium III|पेंटियम III]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />[[VIA Technologies|VIA]] [[Cyrix III|सिरिक्स III]]<br />[[VIA Technologies|VIA]] [[VIA C3|C3]] | ||
| Desktop | | Desktop | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 228: | Line 228: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 423|सॉकेट 423]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 423|सॉकेट 423]] | ||
| 2000 | | 2000 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium 4]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium 4|पेंटियम 4]] | ||
| Desktop | | Desktop | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 238: | Line 238: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 495|सॉकेट 495]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 495|सॉकेट 495]] | ||
| 2000 | | 2000 | ||
| इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III]] | | इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium III|पेंटियम III]] | ||
| Notebook | | Notebook | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 258: | Line 258: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 478|सॉकेट 478]]/<br />[[Socket N|सॉकेट N]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 478|सॉकेट 478]]/<br />[[Socket N|सॉकेट N]] | ||
| 2001 | | 2001 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium 4]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[P4EE#Extreme Edition| | | इंटेल [[Pentium 4|पेंटियम 4]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[P4EE#Extreme Edition|पेंटियम 4 EE]]<br />इंटेल [[List of Intel Pentium 4 processors#Mobile processors|पेंटियम 4 M]] | ||
| Desktop | | Desktop | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 308: | Line 308: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 479|सॉकेट 479]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket 479|सॉकेट 479]] | ||
| 2003 | | 2003 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium M]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron M]] | | इंटेल [[Pentium M|पेंटियम M]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron M]] | ||
| Notebook | | Notebook | ||
| [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | | [[Pin grid array|पीजीए]] | ||
| Line 328: | Line 328: | ||
! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 775]]/<br />[[Socket T|सॉकेट T]] | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 775]]/<br />[[Socket T|सॉकेट T]] | ||
| 2004 | | 2004 | ||
| इंटेल [[Pentium 4]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium D]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron D]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium Extreme Edition| | | इंटेल [[Pentium 4|पेंटियम 4]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium D|पेंटियम D]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron]]<br />इंटेल [[Celeron D]]<br />इंटेल [[Pentium Extreme Edition|पेंटियम XE]]<br />इंटेल [[Core 2 Duo]]<br />इंटेल [[Core 2 Quad]]<br />इंटेल [[Xeon]] | ||
| Desktop | | Desktop | ||
| [[Land grid array|LGA]] | | [[Land grid array|LGA]] | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 27 December 2022
कम्पुटर हार्डवेयर (जिसे छूकर अनुभूत किया जा सके) में, एक सीपीयू सॉकेट या सीपीयू स्लॉट में एक या एक से अधिक यांत्रिक घटक होते हैं जो एक माइक्रोप्रोसेसर और एक मुद्रित सर्किट बोर्ड (पीसीबी) के बीच यांत्रिक और विद्युत कनेक्शन प्रदान करते हैं। यह सोल्डरिंग के बिना सेंट्रल प्रोसेसिंग यूनिट (सीपीयू) को रखने और बदलने की अनुमति देता है।
सामान्य सॉकेट्स में रिटेंशन क्लिप्स होती हैं जो एक स्थिर बल लगाती हैं, जिसे डिवाइस डालने पर दूर किया जाना चाहिए। कई पिन वाले चिप्स के लिए, शून्य सम्मिलन बल (ZIF) सॉकेट को प्राथमिकता दी जाती है। सामान्य सॉकेट्स में पिन ग्रिड ऐरे (पीजीए) या लैंड ग्रिड ऐरे (एलजीए) शामिल हैं। एक बार एक हैंडल (पीजीए प्रकार) या एक सतह प्लेट (एलजीए प्रकार) लगाने के बाद ये डिज़ाइन एक संपीड़न (भौतिकी) लागू करते हैं। सॉकेट में चिप डालने पर सीसा (इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स) को झुकने के जोखिम से बचने के दौरान यह बेहतर यांत्रिक प्रतिधारण प्रदान करता है। कुछ उपकरण बॉल ग्रिड ऐरे (बीजीए) सॉकेट का उपयोग करते हैं, हालांकि इन्हें सोल्डरिंग की आवश्यकता होती है और आमतौर पर इन्हें उपयोगकर्ता द्वारा बदली जाने योग्य नहीं माना जाता है।
CPU सॉकेट का उपयोग डेस्कटॉप और सर्वर (कंप्यूटिंग) कंप्यूटर में मदरबोर्ड पर किया जाता है। क्योंकि वे घटकों की आसान अदला-बदली की अनुमति देते हैं, उनका उपयोग नए सर्किट के प्रोटोटाइप के लिए भी किया जाता है। लैपटॉप आमतौर पर सरफेस-माउंट सीपीयू का उपयोग करते हैं, जो सॉकेट वाले हिस्से की तुलना में मदरबोर्ड पर कम स्थान लेते हैं।
जैसे-जैसे आधुनिक सॉकेट में पिन घनत्व बढ़ता है, प्रिंटेड सर्किट बोर्ड फैब्रिकेशन तकनीक पर बढ़ती मांगों को रखा जाता है, जो बड़ी संख्या में संकेतों को पास के घटकों में सफलतापूर्वक रूट करने की अनुमति देता है। इसी प्रकार, चिप वाहक के अन्दर, पिन की संख्या और पिन घनत्व बढ़ने के साथ तार का जोड़ तकनीक की भी अधिक मांग हो जाती है। प्रत्येक सॉकेट प्रौद्योगिकी में विशिष्ट रिफ्लो सोल्डरिंग (इलेक्ट्रॉनिक उपकरणों में एक लेप लगाकर टाँका लगाना) आवश्यकताएं होंगी। जैसे ही सीपीयू और मेमोरी फ्रीक्वेंसी 30 मेगाहर्ट्ज या उसके ऊपर बढ़ती है, इलेक्ट्रिकल सिग्नलिंग तेजी से समानांतर बसों पर अंतर संकेतन में शिफ्ट हो जाती है, जिससे संकेत की समग्रता चुनौतियों का एक नया सेट आ जाता है। सीपीयू सॉकेट का विकास इन सभी प्रौद्योगिकियों के साथ-साथ विकास के समान है।
आधुनिक सीपीयू सॉकेट लगभग हमेशा ताप सिंक माउंटिंग सिस्टम, या कम बिजली उपकरणों, अन्य थर्मल विचारों के संयोजन के साथ डिजाइन किए जाते हैं।
फंक्शन
एक सीपीयू सॉकेट प्लास्टिक से बना होता है, और अक्सर लीवर या कुंडी के साथ आता है, और सीपीयू पर प्रत्येक पिन या लैंड के लिए धातु के संपर्क के साथ आता है। सीपीयू के उचित सम्मिलन को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कई पैकेजों की कुंजी है। पीजीए (पिन ग्रिड ऐरे) पैकेज वाले सीपीयू को सॉकेट में डाला जाता है और यदि शामिल किया जाता है, तो कुंडी बंद हो जाती है। लैंड ग्रिड एरे वाले पैकेज वाले सीपीयू को सॉकेट में डाला जाता है, लैच प्लेट को सीपीयू के ऊपर की स्थिति में फ़्लिप किया जाता है, और लीवर को नीचे किया जाता है और सीपीयू के संपर्कों को सॉकेट की भूमि के खिलाफ मजबूती से दबाना और एक अच्छा कनेक्शन सुनिश्चित करने के साथ-साथ यांत्रिक स्थिरता में वृद्धि करना।
सीपीयू सॉकेट्स और स्लॉट्स की सूची
80x86
टेबल लेजेंड:
| सॉकेट
नाम |
परिचय का वर्ष | सीपीयू परिवारों ने समर्थन किया | कंप्यूटर प्रकार | पैकेट | पिन की गिनती | पिन पिच
(मिमी) |
बस घड़ी & स्थानांतरण |
नोट्स |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| डीआईपी | 1970s | इंटेल 8086 इंटेल 8088 |
डीआईपी | 40 | 2.54 | 5/10 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| पीएलसीसी | ? | इंटेल 80186 इंटेल 80286 इंटेल 80386 |
पीएलसीसी | 68 to 132 | 1.27 | 6–40 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| पीजीए 168 | ? | इंटेल 80486 एएमडी 486 सिरिक्स 486 |
पीजीए | 168 | 2.54 | 16–50 मेगाहर्ट्ज | कभी-कभी सॉकेट 0 या सॉकेट 486 के रूप में जाना जाता है | |
| सॉकेट 1 | 1989 | इंटेल 80486 एएमडी 486 एएमडी 5x86 सिरिक्स 486 सिरिक्स 5x86 |
पीजीए | 169 | 2.54 | 16–50 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| सॉकेट 2 | ? | इंटेल 80486 इंटेल पेंटियम Overdrive (P24T) इंटेल DX4 एएमडी 486 एएमडी 5x86 सिरिक्स 486 सिरिक्स 5x86 |
पीजीए | 238 | 2.54 | 16–50 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| सॉकेट 3 | 1991 | इंटेल 80486 इंटेल पेंटियम Overrdrive (P24T) इंटेल DX4 एएमडी 486 एएमडी 5x86 सिरिक्स 486 सिरिक्स 5x86 IBM Blue Lightning |
पीजीए | 237 | 2.54 | 16–50 मेगाहर्ट्ज[lower-alpha 1] | ||
| सॉकेट 4 | 1993 | इंटेल पेंटियम | पीजीए | 273 | ? | 60–100 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| सॉकेट 5 | 1994 | इंटेल पेंटियम एएमडी K5 सिरिक्स 6x86 IDT WinChip C6 IDT WinChip 2 |
पीजीए | 320 | ? | 50–100 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| सॉकेट 6 | ? | इंटेल 80486 | पीजीए | 235 | ? | ? | Designed but not used | |
| सॉकेट 463/ सॉकेट NexGen |
1994 | NexGen Nx586 | पीजीए | 463 | ? | 37.5–66 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| सॉकेट 7 | 1994 | इंटेल पेंटियम इंटेल पेंटियम MMX एएमडी K6 |
पीजीए | 321 | ? | 50–66 मेगाहर्ट्ज | It is possible to use सॉकेट 7 processors in a सॉकेट 5. An adapter is required, or if one is careful, a socket 7 can be pulled off its pins and put onto a socket 5 board, allowing the use of socket 7 processors. | |
| सॉकेट 8 | 1995 | इंटेल पेंटियम Pro | पीजीए | 387 | ? | 60–66 मेगाहर्ट्ज | ||
| Slot 1 | 1997 | इंटेल पेंटियम II इंटेल पेंटियम III |
Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 66–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Celeron (Covington, Mendocino) पेंटियम II (Klamath, Deschutes) पेंटियम III (Katmai)- all versions पेंटियम III (coppermine) |
| Super सॉकेट 7 | 1998 | एएमडी K6-2 एएमडी K6-III Rise mP6 सिरिक्स MII |
पीजीए | 321 | ? | 66–100 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Backward compatible with Socket 5 and Socket 7 processors. | |
| Slot 2 | 1998 | इंटेल पेंटियम II Xeon इंटेल पेंटियम III Xeon |
Server | Slot | 330 | ? | 100–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 615 | 1999 | इंटेल Mobile पेंटियम II इंटेल Mobile Celeron |
Notebook | पीजीए | 615 | ? | 66 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| Slot A | 1999 | एएमडी Athlon | Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 100 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 370 | 1999 | इंटेल पेंटियम III इंटेल Celeron VIA सिरिक्स III VIA C3 |
Desktop | पीजीए | 370 | 1.27[1] | 66–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट A/ सॉकेट 462 |
2000 | एएमडी Athlon एएमडी Duron एएमडी Athlon XP एएमडी Athlon XP-M एएमडी Athlon MP एएमडी Sempron |
Desktop | पीजीए | 462 | ? | 100–200 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400 MT/s[lower-alpha 2] |
|
| सॉकेट 423 | 2000 | इंटेल पेंटियम 4 | Desktop | पीजीए | 423 | 1[2] | 100 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400 MT/s |
Willamette core only. Can accept some of Socket 478 CPU with an adapter |
| सॉकेट 495 | 2000 | इंटेल Celeron इंटेल पेंटियम III |
Notebook | पीजीए | 495 | 1.27[3] | 66–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 603 | 2001 | इंटेल Xeon | Server | पीजीए | 603 | 1.27[4] | 100–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400–533 MT/s |
|
| सॉकेट 478/ सॉकेट N |
2001 | इंटेल पेंटियम 4 इंटेल Celeron इंटेल पेंटियम 4 EE इंटेल पेंटियम 4 M |
Desktop | पीजीए | 478 | 1.27[5] | 100–200 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400–800 MT/s |
|
| सॉकेट 563 | 2002 | एएमडी Athlon XP-M | Notebook | पीजीए | 563 | ? | 333 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 604 | 2002 | इंटेल Xeon | Server | पीजीए | 604 | 1.27[4] | 100–266 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400–1066 MT/s |
|
| सॉकेट 754 | 2003 | एएमडी Athlon 64 एएमडी Sempron एएमडी Turion 64 |
Desktop | पीजीए | 754 | 1.27[6] | 200–800 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 940 | 2003 | एएमडी Opteron एएमडी Athlon 64 FX |
Desktop Server |
पीजीए | 940 | 1.27[7] | 200–1000 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 479 | 2003 | इंटेल पेंटियम M इंटेल Celeron M |
Notebook | पीजीए | 479[8] | ? | 100–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज 400–533 MT/s |
|
| सॉकेट 939 | 2004 | एएमडी Athlon 64 एएमडी Athlon 64 FX एएमडी Athlon 64 X2 एएमडी Opteron |
Desktop | पीजीए | 939 | 1.27[9] | 200–1000 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Support of Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz Support of Opteron limited to 100-series only |
| LGA 775/ सॉकेट T |
2004 | इंटेल पेंटियम 4 इंटेल पेंटियम D इंटेल Celeron इंटेल Celeron D इंटेल पेंटियम XE इंटेल Core 2 Duo इंटेल Core 2 Quad इंटेल Xeon |
Desktop | LGA | 775 | 1.09 x 1.17[10] | 1600 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Can accept LGA 771 CPU with slight modification and use of an adapter |
| सॉकेट M | 2006 | इंटेल Core Solo इंटेल Core Duo इंटेल Dual-Core Xeon इंटेल Core 2 Duo |
Notebook | पीजीए | 478 | ? | 133–166 मेगाहर्ट्ज 533–667 MT/s |
Replaces Socket 479 |
| LGA 771/ सॉकेट J |
2006 | इंटेल Xeon | Server | LGA | 771 | 1.09 x 1.17[11] | 1600 मेगाहर्ट्ज | See LGA 775/Socket T above |
| सॉकेट S1 | 2006 | एएमडी Turion 64 X2 | Notebook | पीजीए | 638 | 1.27[12] | 200–800 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
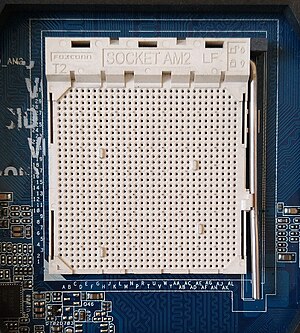
| सॉकेट AM2 | 2006 | एएमडी Athlon 64 एएमडी Athlon 64 X2 |
Desktop | पीजीए | 940 | 1.27[9] | 200–1000 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Replaces Socket 754 and Socket 939 |
| सॉकेट F/ सॉकेट L (सॉकेट 1207FX) |
2006 | एएमडी Athlon 64 FX एएमडी Opteron (Socket L only support Athlon 64 FX) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1207 | 1.1[13] | Socket L: 1000 मेगाहर्ट्ज in Single CPU mode, 2000 मेगाहर्ट्ज in Dual CPU mode |
Replaces Socket 940 Socket L was intended for enthusiasts who wanted server power in a desktop PC. It is just a re-branded Socket F that doesn't need special RAM, and may have only been used in the Asus L1N64-SLI WS Motherboard. |
| सॉकेट AM2+ | 2007 | एएमडी Athlon 64 एएमडी Athlon X2 एएमडी Phenom एएमडी Phenom II |
Desktop | पीजीए | 940 | 1.27[9] | 200–2600 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2 AM2+ Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2 AM2 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2+ |
| सॉकेट P | 2007 | इंटेल Core 2 | Notebook | पीजीए | 478 | ? | 133–266 मेगाहर्ट्ज 533–1066 MT/s |
Replaces Socket M |
| LGA 1366/ सॉकेट B |
2008 | इंटेल Core i7 (900 series) इंटेल Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1366 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Replaces Socket J (LGA 771) in the entry level. |
| सॉकेट AM3 | 2009 | एएमडी Phenom II एएमडी Athlon II एएमडी Sempron एएमडी Opteron (1300 series) |
Desktop | पीजीए | 941[14] or 940[15] | 1.27[9] | 200–3200 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2+ AM3 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2/AM2+ Sempron 140 only |
| rपीजीए 988A/ सॉकेट G1 |
2009 | इंटेल Clarksfield इंटेल Arrandale |
Notebook | rपीजीए | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s | Replaces Socket P |
| LGA 1156/ सॉकेट H |
2009 | इंटेल Nehalem (1st gen) इंटेल Westmere |
Desktop | LGA | 1156 | ? | 2.5 GT/s | DMI bus is a (perhaps modified) PCIe x4 v1.1 interface |
| सॉकेट G34 | 2010 | एएमडी Opteron (6000 series) | Server | LGA | 1974 | ? | 200–3200 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Replaces Socket F |
| सॉकेट C32 | 2010 | एएमडी Opteron (4000 series) | Server | LGA | 1207 | ? | 200–3200 मेगाहर्ट्ज | Replaces Socket F, Socket AM3 |
| LGA 1567/ सॉकेट LS |
2010 | इंटेल Xeon 6500/7500-series | Server | LGA | 1567 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | |
| LGA 1155/ सॉकेट H2 |
2011/Q1 2011.01.09 |
इंटेल Sandy Bridge (2nd gen) इंटेल Ivy Bridge (3rd gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1155 | ? | 5.7 GT/s | used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors.
Sandy Bridge supports 20 PCIe 2.0 lanes. |
| LGA 2011/ सॉकेट R |
2011/Q3 2011.11.14 |
इंटेल Core i7 3xxx Sandy Bridge-E इंटेल Core i7 4xxx Ivy Bridge-E इंटेल Xeon E5 2xxx/4xxx (Sandy Bridge EP) (2/4S) इंटेल Xeon E5-2xxx/4xxx v2 (Ivy Bridge EP) (2/4S) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2011 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP both support 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Using the Xeon focused 2011 socket gives also 4 memory Channels. |
| rपीजीए 988B/ सॉकेट G2 |
2011 | इंटेल Core i7 (2000, 3000 series) इंटेल Core i5 (2000, 3000 series) इंटेल Core i3 (2000, 3000 series) |
Notebook | rपीजीए | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s, 4.8 GT/s | |
| सॉकेट FM1 | 2011 | एएमडी Llano Processors | Desktop | पीजीए | 905 | 1.27 | 5.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation APUs |
| सॉकेट FS1 | 2011 | एएमडी Llano Processors | Notebook | पीजीए | 722 | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation Mobile APUs |
| सॉकेट AM3+ | 2011 | एएमडी FX Vishera एएमडी FX Zambezi एएमडी Phenom II एएमडी Athlon II एएमडी Sempron |
Desktop | पीजीए | 942 (CPU 71pin) | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | |
| LGA 1356/ सॉकेट B2 |
2012 | इंटेल Xeon (E5 1400 & 2400 series) | Server | LGA | 1356 | ? | 3.2–4.0 GT/s | |
| सॉकेट FM2 | 2012 | एएमडी Trinity Processors | Desktop | पीजीए | 904 | 1.27 | ? | used for 2nd generation APUs |
| LGA 1150/ सॉकेट H3 |
2013 | इंटेल Haswell (4th gen) इंटेल Haswell Refresh इंटेल Broadwell (5th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1150 | ? | ? | used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors |
| rपीजीए 946B/947/ सॉकेट G3 |
2013 | इंटेल Haswell | Notebook | rपीजीए | 946 | 1 | 5.0 GT/s | |
| सॉकेट FM2+ | 2014 | एएमडी Kaveri एएमडी Godavari |
Desktop | पीजीए | 906 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD Accelerated Processing Units (APUs) such as "Richland" and "Trinity" |
| सॉकेट AM1 | 2014 | एएमडी Athlon एएमडी Sempron |
Desktop | पीजीए | 721 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD Accelerated Processing Units (APUs) such as "Kabini" |
| LGA 2011-v3 | 2014 (August and September) |
Haswell-E Haswell-EP |
Desktop | LGA | 2011 | ? | Up to 68 GB/sec. Depends on DDR4 speed and channel count. |
Up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Up to 4 memory Channels. |
| LGA 1151/ सॉकेट H4 |
2015 | इंटेल Skylake (6th gen) इंटेल Kaby Lake (7th gen) इंटेल Coffee Lake (8th gen) इंटेल Coffee Lake Refresh (9th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1151 | ? | 5 GT/s - 8 GT/s | used for Intel's 6th generation (Skylake), 7th generation (Kaby Lake), 8th generation (Coffee Lake) processors, and 9th generation (Coffee Lake Refresh) processors |
| LGA 3647 | 2016 | इंटेल Xeon Phi इंटेल Skylake-SP |
Server | LGA | 3647 | ? | ? | used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors |
| सॉकेट AM4 | 2017 | एएमडी Ryzen 9 एएमडी Ryzen 7 एएमडी Ryzen 5 एएमडी Ryzen 3 Athlon 200 |
Desktop | पीजीए | 1331 | 1 | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen 9, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 5 & Ryzen 3 Zen based processors |
| सॉकेट SP3 | 2017 | एएमडी Epyc | Server | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Epyc processors |
| सॉकेट TR4/ सॉकेट SP3r2 |
2017 | एएमडी Ryzen Threadripper | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 2066/ सॉकेट R4 |
2017 | इंटेल Skylake-X इंटेल Kaby Lake-X इंटेल Cascade Lake-X |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2066 | ? | ? | Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors |
| सॉकेट sTRX4/ सॉकेट SP3r3 |
2019 | एएमडी Ryzen Threadripper (3000 series) | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 4189 | 2020 | इंटेल Cooper Lake इंटेल Ice Lake-SP |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 4189[16] | 0.99[16] | ||
| LGA 1200 | 2020 | इंटेल Comet Lake (10th gen) इंटेल Rocket Lake (11th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1200 | |||
| LGA 1700 | 2021 | इंटेल Alder Lake (12th gen) | Desktop | LGA | 1700 | |||
| LGA 1700 | 2022 | इंटेल Raptor Lake (13th gen) | Desktop | LGA | 1700 | |||
| सॉकेट AM5 | 2022 | एएमडी Ryzen 7000 series | Desktop | LGA | 1718 | Zen 4 Ryzen CPUs | ||
| सॉकेट SP5 | 2022 (planned) | एएमडी Epyc Genoa | Server | LGA | 6096 | Used for Epyc Genoa and Milan | ||
| LGA 4677 | 2022 (planned) | इंटेल Sapphire Rapids | Server | LGA | 4677 | |||
| सॉकेट name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
अन्य निर्देश सेट आर्किटेक्चर
| सॉकेट name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daughter Card | 1995 | PowerPC 601+ | Desktop | Slot | 146 | ? | 40-60 Hz | |
| सॉकेट 288 | ? | PowerPC 603+ | Desktop | पीजीए | 288 | ? | 40-60 Hz | |
| सॉकेट 431 | 1995 | Alpha 21064/21064A | Desktop | पीजीए | 431 | ? | 12.5–66.67 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 499 | 1997 | Alpha 21164/21164A | Desktop | पीजीए | 499 | ? | 15–100 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| सॉकेट 587 | 1998 | Alpha 21264 | Desktop | पीजीए | 587 | ? | 12.5–133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| Slot B | 1999 | Alpha 21264/21264A | Desktop | Slot | 587 | ? | 100 मेगाहर्ट्ज[17] | |
| PAC418 | 2001 | इंटेल Itanium | Server | पीजीए | 418 | ? | 133 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| PAC611 | 2002 | इंटेल Itanium 2 HP PA-8800, PA-8900 |
Server | पीजीए | 611 | ? | 200 मेगाहर्ट्ज | |
| LGA 1248 | 2010 | इंटेल Itanium 9300-series and up | Server | LGA | 1248 | ? | 4.8-6.4 GT/s | |
| सॉकेट name |
Year of introduction | CPU families supported | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
स्लॉट्स
बस-संगत स्लॉट मदरबोर्ड में सॉकेट प्रोसेसर का उपयोग करने के लिए स्लॉटकेट विशेष एडेप्टर हैं।
यह भी देखें
संदर्भ
- ↑ "Intel 815 Chipset Family" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 4, 2009.
- ↑ "423 Pin Socket (PGA423) Design Guidelines" (PDF). Intel. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 29, 2009. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "495-Pin and 615-pin micro-PGA ZIF Socket Design Specification Application Note" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "mPGA 604 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "Intel Pentium 4 Processor 478-Pin Socket (mPGA478) Design Guidelines" (PDF). Intel (in English). Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "AMD Sempron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "AMD Opteron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD (in English). Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ CPU only has 478 pins, but the socket has 479.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "AMD Opteron Processor Product Data Sheet" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "LGA 775 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel (in English). Retrieved May 4, 2009.
- ↑ "LGA771 Socket Mechanical Design Guide" (PDF). Intel (in English). Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "Low-Profile Socket S1 Design Specification" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ↑ "Thermal Design Guide for Socket F (1207) Processors" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ↑ CPU only has 938 pins, but the socket has 941.
- ↑ AMD Documentation "Socket AM3 design Specification" (PDF). AMD. Retrieved January 5, 2012.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "LGA 4189 Socket and Hardware" (PDF).
- ↑ Hachman, Mark (February 2, 1999). "Alpha camp moves to "Slot B" connector to push further into workstations". EE Times (in English). Retrieved November 10, 2022.
बाहरी कड़ियाँ
- Socket ID Guide
- CPU Sockets Chart - A fairly detailed table listing x86 Sockets and associated attributes.
- techPowerUp! CPU Database
- Processor sockets