ऑब्जेक्ट-मॉडलिंग तकनीक: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:OMT object diagram.png|thumb|240px|ओएमटी ऑब्जेक्ट आरेख]] | [[Image:OMT object diagram.png|thumb|240px|ओएमटी ऑब्जेक्ट आरेख]] | ||
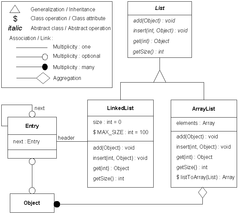
[[Image:OMT state diagram.png|thumb|360px|ओएमटी [[राज्य आरेख|स्थिति आरेख]]]]'''ऑब्जेक्ट-मॉडलिंग तकनीक''' (ओएमटी) [[कंप्यूटर सॉफ्टवेयर]] मॉडलिंग और डिजाइनिंग के लिए एक [[ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडलिंग भाषा]] दृष्टिकोण है। इसे 1991 के आसपास [[जेम्स रंबॉघ]], ब्लाहा, प्रीमेरलानी, एडी और लोरेन्सन द्वारा ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड विश्लेषण और डिज़ाइन या ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड सिस्टम विकसित करने और [[ ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग ]] का समर्थन करने की एक विधि के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। ओएमटी सिस्टम के ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडल या स्थिर संरचना का वर्णन करता है। | [[Image:OMT state diagram.png|thumb|360px|ओएमटी [[राज्य आरेख|स्थिति आरेख]]]]'''ऑब्जेक्ट-मॉडलिंग तकनीक''' (ओएमटी) [[कंप्यूटर सॉफ्टवेयर]] मॉडलिंग और डिजाइनिंग के लिए एक [[ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडलिंग भाषा]] दृष्टिकोण है। इसे 1991 के आसपास [[जेम्स रंबॉघ]], ब्लाहा, प्रीमेरलानी, एडी और लोरेन्सन द्वारा ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड विश्लेषण और डिज़ाइन या ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड सिस्टम विकसित करने और [[ ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग |ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग]] का समर्थन करने की एक विधि के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। ओएमटी सिस्टम के ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडल या स्थिर संरचना का वर्णन करता है। | ||
ओएमटी को सॉफ्टवेयर विकास के एक दृष्टिकोण के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। रूंबॉ के अनुसार मॉडलिंग के उद्देश्य हैं:<ref>Rumbaugh et al. (1991:15)</ref><ref name="Tot97">Terje Totland (1997). [http://www.idi.ntnu.no/grupper/su/publ/html/totland/ch0527.htm 5.2.7 Object Modeling Technique (OMT)] Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim.</ref> | ओएमटी को सॉफ्टवेयर विकास के एक दृष्टिकोण के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। रूंबॉ के अनुसार मॉडलिंग के उद्देश्य हैं:<ref>Rumbaugh et al. (1991:15)</ref><ref name="Tot97">Terje Totland (1997). [http://www.idi.ntnu.no/grupper/su/publ/html/totland/ch0527.htm 5.2.7 Object Modeling Technique (OMT)] Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim.</ref> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*कार्यात्मक मॉडल: कार्यात्मक मॉडल मॉडल के प्रक्रिया परिप्रेक्ष्य को संभालता है, जो समान्य रूप से डेटा प्रवाह आरेखों के अनुरूप होता है। मुख्य अवधारणाएँ प्रक्रिया, डेटा संचयन, डेटा प्रवाह और अभिनेता हैं।<ref name="Tot97" /> | *कार्यात्मक मॉडल: कार्यात्मक मॉडल मॉडल के प्रक्रिया परिप्रेक्ष्य को संभालता है, जो समान्य रूप से डेटा प्रवाह आरेखों के अनुरूप होता है। मुख्य अवधारणाएँ प्रक्रिया, डेटा संचयन, डेटा प्रवाह और अभिनेता हैं।<ref name="Tot97" /> | ||
ओएमटी [[ एकीकृत मॉडलिंग भाषा ]] (यूएमएल) का पूर्ववर्ती है। कई ओएमटी मॉडलिंग तत्व यूएमएल के लिए सामान्य हैं। | ओएमटी [[ एकीकृत मॉडलिंग भाषा |एकीकृत मॉडलिंग भाषा]] (यूएमएल) का पूर्ववर्ती है। कई ओएमटी मॉडलिंग तत्व यूएमएल के लिए सामान्य हैं। | ||
ओएमटी में कार्यात्मक मॉडल: संक्षेप में, ओएमटी में एक कार्यात्मक मॉडल डेटा फ्लो डायग्राम (डीएफडी) की मदद से एक मॉडल में संपूर्ण आंतरिक प्रक्रियाओं के कार्य को परिभाषित करता है। यह विवरण देता है कि प्रक्रियाएं स्वतंत्र रूप से कैसे निष्पादित की जाती हैं। | ओएमटी में कार्यात्मक मॉडल: संक्षेप में, ओएमटी में एक कार्यात्मक मॉडल डेटा फ्लो डायग्राम (डीएफडी) की मदद से एक मॉडल में संपूर्ण आंतरिक प्रक्रियाओं के कार्य को परिभाषित करता है। यह विवरण देता है कि प्रक्रियाएं स्वतंत्र रूप से कैसे निष्पादित की जाती हैं। | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*[http://www.idi.ntnu.no/grupper/su/publ/html/totland/ch0527.htm A short introduction to OMT] | *[http://www.idi.ntnu.no/grupper/su/publ/html/totland/ch0527.htm A short introduction to OMT] | ||
The model is defined by the organization’s vision, mission, and values, as well as sets of boundaries for the organization—what products or services it will deliver, what customers or markets it will target, and what supply and delivery channels it will use. While the business model includes high-level strategies and tactical direction for how the organization will implement the model, it also includes the annual goals that set the specific steps the organization intends to undertake in the next year and the measures for their expected accomplishment. Each of these is likely to be part of internal documentation that is available to the internal auditor. | The model is defined by the organization’s vision, mission, and values, as well as sets of boundaries for the organization—what products or services it will deliver, what customers or markets it will target, and what supply and delivery channels it will use. While the business model includes high-level strategies and tactical direction for how the organization will implement the model, it also includes the annual goals that set the specific steps the organization intends to undertake in the next year and the measures for their expected accomplishment. Each of these is likely to be part of internal documentation that is available to the internal auditor. | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Object-Modeling Technique}} | |||
[[Category: ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग]] | |||
[[Category: एकीकृत मॉडलिंग भाषा]] | |||
{{uml-stub}} | {{uml-stub}} | ||
Revision as of 08:04, 18 July 2023

ऑब्जेक्ट-मॉडलिंग तकनीक (ओएमटी) कंप्यूटर सॉफ्टवेयर मॉडलिंग और डिजाइनिंग के लिए एक ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडलिंग भाषा दृष्टिकोण है। इसे 1991 के आसपास जेम्स रंबॉघ, ब्लाहा, प्रीमेरलानी, एडी और लोरेन्सन द्वारा ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड विश्लेषण और डिज़ाइन या ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड सिस्टम विकसित करने और ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग का समर्थन करने की एक विधि के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। ओएमटी सिस्टम के ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडल या स्थिर संरचना का वर्णन करता है।
ओएमटी को सॉफ्टवेयर विकास के एक दृष्टिकोण के रूप में विकसित किया गया था। रूंबॉ के अनुसार मॉडलिंग के उद्देश्य हैं:[1][2]
- भौतिक संस्थाओं का निर्माण (सिमुलेशन) करने से पहले उनका परीक्षण करना,
- ग्राहकों के साथ संचार,
- विज़ुअलाइज़ेशन (सूचना की वैकल्पिक प्रस्तुति), और
- जटिलता में कमी.
ओएमटी ने तीन मुख्य प्रकार के मॉडल प्रस्तावित किए हैं:
- ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडल: ऑब्जेक्ट मॉडल मॉडल किए गए डोमेन में स्थिर और सबसे स्थिर घटनाओं का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।[3] मुख्य अवधारणाएँ गुण और संचालन के साथ वर्ग और जुड़ाव हैं। एकत्रीकरण और सामान्यीकरण (एकाधिक वंशानुक्रम के साथ) पूर्वनिर्धारित संबंध हैं।[2]
- गतिशील मॉडल: गतिशील मॉडल मॉडल पर एक स्थिति/संक्रमण दृश्य का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। मुख्य अवधारणाएँ अवस्था, अवस्थाओ के बीच संक्रमण और संक्रमण को गति देने वाली घटनाएँ हैं। कार्रवाइयों को अवस्थाओ के अंदर होने वाले मॉडल के रूप में तैयार किया जा सकता है। सामान्यीकरण और एकत्रीकरण (संगामिति) पूर्वनिर्धारित संबंध हैं।[2]
- कार्यात्मक मॉडल: कार्यात्मक मॉडल मॉडल के प्रक्रिया परिप्रेक्ष्य को संभालता है, जो समान्य रूप से डेटा प्रवाह आरेखों के अनुरूप होता है। मुख्य अवधारणाएँ प्रक्रिया, डेटा संचयन, डेटा प्रवाह और अभिनेता हैं।[2]
ओएमटी एकीकृत मॉडलिंग भाषा (यूएमएल) का पूर्ववर्ती है। कई ओएमटी मॉडलिंग तत्व यूएमएल के लिए सामान्य हैं।
ओएमटी में कार्यात्मक मॉडल: संक्षेप में, ओएमटी में एक कार्यात्मक मॉडल डेटा फ्लो डायग्राम (डीएफडी) की मदद से एक मॉडल में संपूर्ण आंतरिक प्रक्रियाओं के कार्य को परिभाषित करता है। यह विवरण देता है कि प्रक्रियाएं स्वतंत्र रूप से कैसे निष्पादित की जाती हैं।
संदर्भ
अग्रिम पठन
- James Rumbaugh, Michael Blaha, William Premerlani, Frederick Eddy, William Lorensen (1994). Object-Oriented Modeling and Design. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-629841-9
- Terry Quatrani, Michael Jesse Chonoles (1996). Succeeding With the Booch and OMT Methods: A Practical Approach. Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-8053-2279-8
बाहरी संबंध
The model is defined by the organization’s vision, mission, and values, as well as sets of boundaries for the organization—what products or services it will deliver, what customers or markets it will target, and what supply and delivery channels it will use. While the business model includes high-level strategies and tactical direction for how the organization will implement the model, it also includes the annual goals that set the specific steps the organization intends to undertake in the next year and the measures for their expected accomplishment. Each of these is likely to be part of internal documentation that is available to the internal auditor.