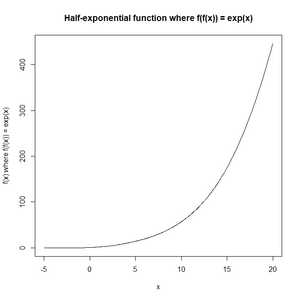
अर्ध-घातांकीय फलन
गणित में, अर्ध-घातांकीय फलन किसी घातांकीय फलन का कार्यात्मक वर्गमूल होता है। यानी फ़ंक्शन (गणित) ऐसा है कि फ़ंक्शन संरचना स्वयं के साथ घातांकीय फ़ंक्शन में परिणत होती है:[1][2]
बंद-फ़ॉर्म सूत्र की असंभवता
यदि कोई फ़ंक्शन मानक अंकगणितीय संचालन, घातांक, लघुगणक और वास्तविक संख्या-मूल्यवान स्थिरांक का उपयोग करके परिभाषित किया गया है, फिर या तो सबएक्सपोनेंशियल या सुपरएक्सपोनेंशियल है।[3] इस प्रकार, हार्डी फ़ील्ड#उदाहरण|हार्डी L-फ़ंक्शन अर्ध-घातांकीय नहीं हो सकता.
निर्माण
किसी भी घातीय फलन को स्व-रचना के रूप में लिखा जा सकता है के अपरिमित रूप से अनेक संभावित विकल्पों के लिए . विशेष रूप से, प्रत्येक के लिए खुले अंतराल में और प्रत्येक सतत कार्य के लिए मोनोटोनिक फ़ंक्शन फ़ंक्शन से विशेषण फलन , इस फ़ंक्शन का निरंतर सख्ती से बढ़ते फ़ंक्शन तक विस्तार है वास्तविक संख्याओं पर जैसे कि .[4] कार्यक्रम कार्यात्मक समीकरण का अद्वितीय समाधान है
सरल उदाहरण, जो की ओर ले जाता है सर्वत्र सतत् प्रथम व्युत्पत्ति का होना, लेना है और , देना
आवेदन
बहुपद और घातांक के बीच मध्यवर्ती विकास दर के लिए कम्प्यूटेशनल जटिलता सिद्धांत में अर्ध-घातीय कार्यों का उपयोग किया जाता है।[2] समारोह यदि यह मोनोटोनिक फ़ंक्शन है, तो कम से कम किसी अर्ध-घातांकीय फ़ंक्शन के रूप में तेजी से बढ़ता है (इसकी संरचना स्वयं के साथ तेजी से बढ़ती है) | गैर-घटती नहीं है और , के लिए every .[5]
यह भी देखें
संदर्भ
- ↑ Kneser, H. (1950). "Reelle analytische Lösungen der Gleichung φ(φ(x) = ex[[Category: Templates Vigyan Ready]] und verwandter Funktionalgleichungen". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik. 187: 56–67. MR 0035385.
{{cite journal}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Miltersen, Peter Bro; Vinodchandran, N. V.; Watanabe, Osamu (1999). "Super-polynomial versus half-exponential circuit size in the exponential hierarchy". In Asano, Takao; Imai, Hiroshi; Lee, D. T.; Nakano, Shin-ichi; Tokuyama, Takeshi (eds.). Computing and Combinatorics, 5th Annual International Conference, COCOON '99, Tokyo, Japan, July 26–28, 1999, Proceedings. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 1627. Springer. pp. 210–220. doi:10.1007/3-540-48686-0_21. MR 1730337.
- ↑ van der Hoeven, J. (2006). Transseries and real differential algebra. Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Vol. 1888. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. doi:10.1007/3-540-35590-1. ISBN 978-3-540-35590-8. MR 2262194. See exercise 4.10, p. 91, according to which every such function has a comparable growth rate to an exponential or logarithmic function iterated an integer number of times, rather than the half-integer that would be required for a half-exponential function.
- ↑ Crone, Lawrence J.; Neuendorffer, Arthur C. (1988). "Functional powers near a fixed point". Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications. 132 (2): 520–529. doi:10.1016/0022-247X(88)90080-7. MR 0943525.
- ↑ Razborov, Alexander A.; Rudich, Steven (1997). "Natural proofs". Journal of Computer and System Sciences. 55 (1): 24–35. doi:10.1006/jcss.1997.1494. MR 1473047.