हाइड्रोआयोडिक एसिड
|
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
आयोडीन[1]
| |||
| Other names
हाइड्रोनियम आयोडाइड
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| HI(aq) | |||
| Molar mass | 127.91 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | acrid | ||
| Density | 1.70 g/mL, azeotrope (57% HI by weight) | ||
| Boiling point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K) 1.03 bar, azeotrope | ||
| Aqueous solution | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | -9.3 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Danger | |||
| H314 | |||
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Hydrofluoric acid Hydrochloric acid Hydrobromic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Hydrogen iodide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
हाइड्रोआयोडिक अम्ल (या हाइड्रोडिक अम्ल) हाइड्रोजन आयोडाइड (एचआई) का जलीय घोल है। यह शक्तिशाली अम्ल है, जो जलीय घोल में पूरी तरह से आयनित होता है। यह रंगहीन होता है। केंद्रित समाधान सामान्यतः 48% से 57% एचआई हैं।[2]
प्रतिक्रियाएं
आयोडीन देने के लिए हाइड्रोआयोडिक अम्ल वायु में ऑक्सीजन के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करता है:
- 4 HI + O2 → 2 H2O + 2 I2
अन्य हाइड्रोजन हैलाइडों की तरह, हाइड्रोआयोडिक अम्ल अल्काइल आयोडाइड्स देने के लिए एल्केन में जोड़ता है। इसे कम करने वाले घटक के रूप में भी उपयोग किया जा सकता है, उदाहरण के लिए नाइट्रो यौगिकों को एनिलिन में कमी होती है।[3]
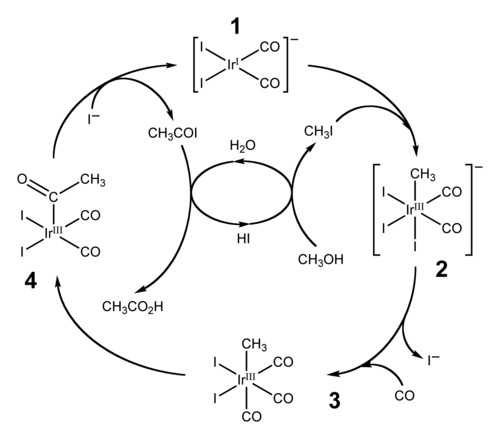
कैटिवा प्रक्रिया
कैटिवा प्रक्रिया हाइड्रोआयोडिक अम्ल का प्रमुख अंतिम उपयोग है, जो मेथनॉल के कार्बोनाइलीकरण द्वारा एसीटिक अम्ल के उत्पादन के लिए सह-उत्प्रेरक के रूप में कार्य करता है।[4][5]
अयुक्त उपयोग
हाइड्रोआयोडिक एसिड को यू.एस. फेडरल डीईए लिस्ट रासायनिक के रूप में सूचीबद्ध किया गया है, इसका उपयोग इफेड्रिन या स्यूडोएफ़ेड्रिन (नेजल डीकॉन्गेस्टेंट गोलियों से पुनर्प्राप्त) से मेथामफेटामाइन के उत्पादन से तत्व कम करने वाले घटक के रूप में किया जाता है।[6]
संदर्भ
- ↑ Template:साइट बुक
- ↑ Lyday, Phyllis A. (2005). "Iodine and Iodine Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 382–390. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_381.
- ↑ Kumar, J. S. Dileep; Ho, ManKit M.; Toyokuni, Tatsushi (2001). "Simple and chemoselective reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to aromatic amines: reduction with hydriodic acid revisited". Tetrahedron Letters. 42 (33): 5601–5603. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)01083-8.
- ↑ Jones, J. H. (2000). "एसिटिक एसिड के निर्माण के लिए कैटिवा प्रक्रिया" (PDF). Platinum Metals Rev. 44 (3): 94–105.
- ↑ Sunley, G. J.; Watson, D. J. (2000). "High productivity methanol carbonylation catalysis using iridium - The Cativa process for the manufacture of acetic acid". Catalysis Today. 58 (4): 293–307. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(00)00263-7.
- ↑ Skinner, Harry F. (1990). "Methamphetamine synthesis via hydriodic acid/Red phosphorus reduction of ephedrine". Forensic Science International. 48 (2): 123–134. doi:10.1016/0379-0738(90)90104-7.